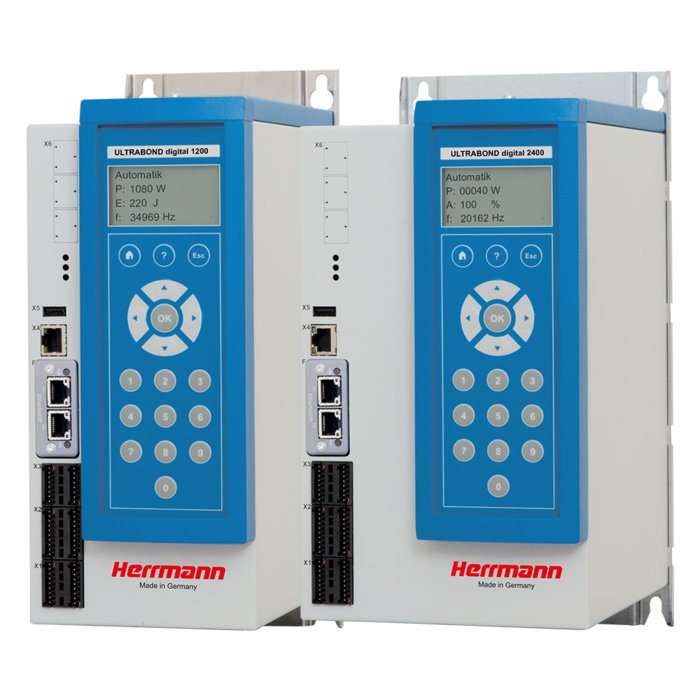
Ultrasonic welding for nonwoven fabrics
Nonwovens consist of individual fibers or endless filaments (fibers of unlimited length) which form a loose cohesion. Nonwovens with thermoplastic fibers (plastics which are shaped when heat is applied) can be welded using ultrasonics. Here, the plastic fiber of the material are introduced to ultrasonic technology where they are heated up, melted, and the nonwovens are bonded together without the use of adhesive.
Key uses and applications
Joining additive-free nonwovens with ultrasonic welding is perfect for hygienic fabrics, medical products, and other consumer applications. Ultrasonic welding of nonwoven fabric is used to:
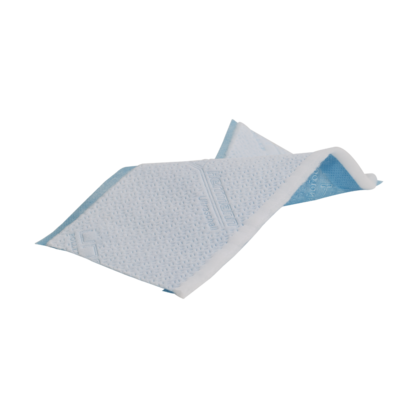
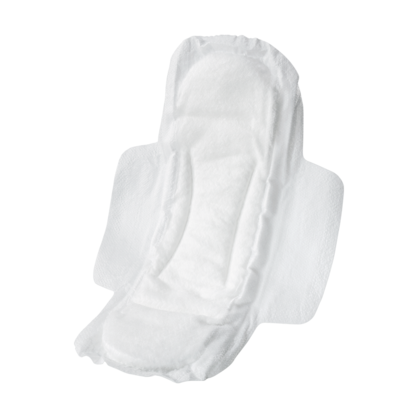
- Laminate various layers together (e.g. for diapers)
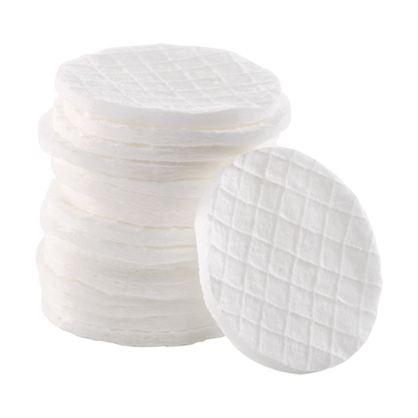
- Incorporate embossing structures (e.g. for cotton pads)
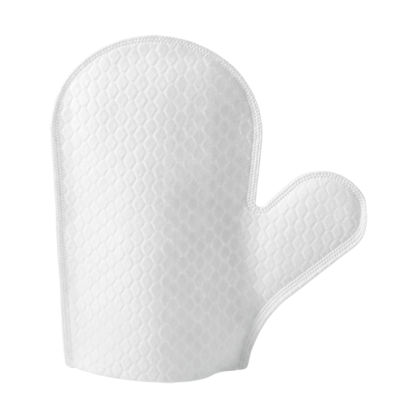
- Separate and hemming of edge areas (e.g. for single-use gloves)
- Perforate web material (e.g. for filter materials)
With ultrasonic welding solutions from Herrmann Ultrasonics, you can emboss, perforate, compact, and cut nonwoven materials. Using rotary tools to create the bond, ultrasonics can make highly consistent bonds in nonwoven fabric at speeds up to 800m/min (2,625 ft/min). This eliminates the need for adhesives, thus preventing any gluing mess, which in turn avoids potential product damage and downtime for cleaning.
Ultimately, this quick and efficient process produces products with a soft feel that should not irritate skin. In addition, by eliminating thread sewing, material is able to maintain a greater elasticity, which helps to contribute towards a superior fit and comfort when used in hygiene applications.








How does it work?
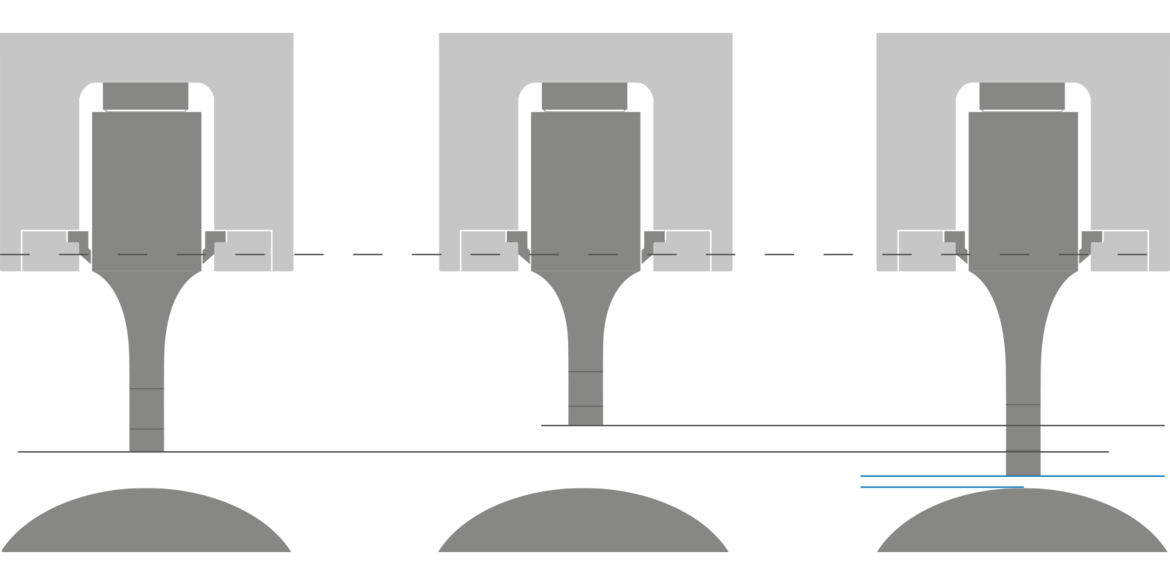
Ultrasonics is created by converting electrical energy in the generator into mechanical vibrations in the converter and ultrasonic stack. This mechanical vibration travels through the ultrasonic stack, through the sonotrode and into the material. The standard frequencies used are between 20 and 35 kHz with an amplitude of 10 to 50 μm. The thermoplastic portion of the material is stimulated, heated up, and melted. The actual weld process is fast: Thanks to the use of rotating tools such as anvil drums, up to 800 m of nonwovens can be processed per minute. The anvil drum has an individual surface structure to focus the ultrasonic energy precisely. This allows for an exact weld through various processes.
A constant distance between the material being processed and the tools is important for optimal results, and this is guaranteed via the precise MICROGAP control technology. It ensures that the distance always remains consistent regardless of the thermal expansion of the tooling during the weld process.
Welding / cross seal
Nonwoven material can be bonded in a cross seal application. As with a longitudinal seal, the sonotrode works in a fixed position without any upward or downward movements. The rotary anvil’s raised cross-directional pattern determines the distance between when the ultrasonics will bond layers of material in the transverse direction. For example, this specific application is used for the side seams of diapers.
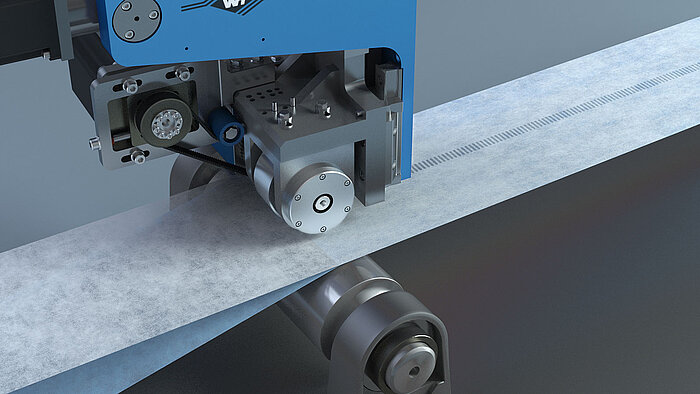
Laminating
The pattern on the rotary anvil determines where the ultrasonics will bond the material. Welding will only occur at the raised pattern points on the anvil, and the other areas will remain unchanged and not bonded. For example, the area not welded on a filter will remain completely breathable.

Embossing
When embossing nonwovens, a unique pattern is pressed and bonded into the layers of material. This unique pattern is based on the anvil design. For example, the pattern shown on cotton pads commonly used for makeup applications can be created through ultrasonically embossing materials.

Perforating
Nonwovens can also be perforated in a defined pattern. The material can be perforated gently with ultrasonics and the anvil drum, for instance, in the case of wound dressings and plasters.
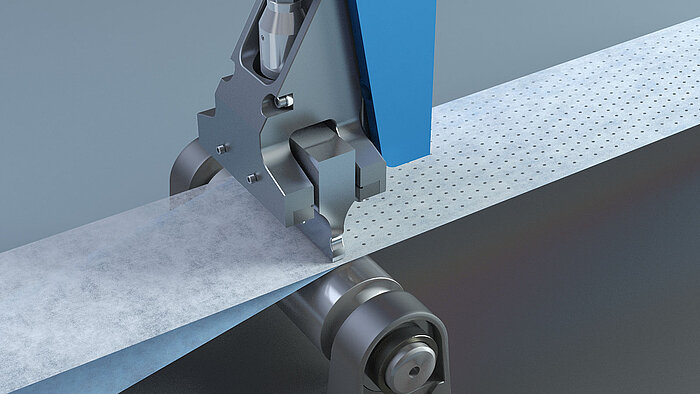
Cutting
Ultrasonics has the ability to cut material while sealing the edge on each side of the cut, known as a cut and seal application. For instance, ultrasonics can cut the shape of a single-use glove out of a roll of material when in production.

Weld geometries
The surface design of an anvil drum is designed to follow an individual application based on the requirements of the products. The energy is focused at the highest point of the anvil drum, and this is where the bonding occurs.
Herrmann Ultrasonics Engineering Capabilities
Herrmann Ultrasonics has the design, development, and integration capabilities to support your product development programs. Our team works with you when integrating our products into your operations. Together, we can help to determine the right system for your processes and how it can save time and resources along the way.
Advantages of Herrmann Ultrasonics Technology
The MICROBOND system offers proven, high quality continuous processing of web material when ultrasonically welding. The patented MICROGAP technology guarantees consistent weld quality at high production speeds and provides user-friendly, simple handling of complex applications.
- Development and production "Made in Germany"
- Patented MICROGAP technology for repeatable, consistent weld quality
- Configurable integration solutions
- Minimization of maintenance and repair costs
- All-round application development consulting – HERRMANN ENGINEERING
Advantages of Herrmann Ultrasonics Modular Systems
The system architecture allows for modular expansion, which can be easily and safely integrated in complex production systems whether a MICROBOND CSI or a MICROBOND RS system is being used.
- Compliance with specified provisions for installation
- Planning documentation (installation guide)
- Detailed interface description
- Modular electrical cabinet solutions
- Plug-in type connection between the electrical cabinet and the MICROBOND actuators









